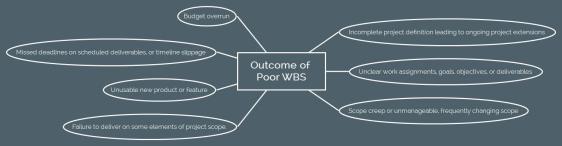
Work breakdown structure (WBS) is an important document in Project management. Poorly constructed WBS will lead to project failure. Here is a mind map that points out different adverse outcomes of poor WBS.
Category Archives: Scope Management
[Video] Summary of Scope Management Processes
Group decision-making techniques
Myth of one man leadership is myth of lone warrior. It is not possible for one person to solve all organizational problems because they are too complex in nature & environment is turbulent. Leaders need a team to solve problem in collaboration instead of solving it in isolation of his own.
We need board of directors to run a company. Group of people to work as team in projects. It is no more a one man show. Issues are everywhere. Each issue needs one solution decision – so group decision-making are inevitable nowadays. Here are some widely used group decision-making methods to reach decision.
What methods & techniques are used in Project Scoping?
One of my blog reader asked me following question – “identify the principles, methods and techniques used for scoping a project?” In reply I wrote a mail explaining all the methods & techniques that is generally practiced for scoping of project. I am sharing the mail content here for everyone’s benefit.
- Project Scope should cover everything that satisfies the customer need
- Arriving final approved scope is very challenging task among all the activities in Project Management
- Defining & Managing Scope is the backbone for Project Management
- It is not a single person’s activity & it involves a group of people mainly project stakeholders. Lot of group interactions will be carried out during the requirement gathering & defining scope
- Scoping is so vital which affects all other important factors in Project like schedule (hence delivery), cost, resources and risks
- Generally high level of scope is available as part of Project Charter
- Enough time need to be given to prepare & review for project scope before approval. Also any scope change after approval is going to affect the Project’s outcome
- It is not necessary that entire project scope should be defined & available at the start of a project. It is progressively elaborated.
Breakdown Structures – A Powerful Project Management Documentation Format
Documentation & maintenance of documentation is one of the hardest and important activities in Project Management. Hundreds of plans, mails, progress tracking, change requests, document updates, contract documents, etc are few examples of documentation events in project life cycle. There are three main formats used to represent information in documents.
1. Text format – This is most used format as we are trained to write paragraphs & pages from our childhood.
2. Tabular format – This is used when a matrix or log type of information representation is required i.e. responsibility matrix, risk log.
3. Tree hierarchical format – This type is used to depict whenever parent-child relationship exists between different elements. This is the prevalent type used in all “Breakdown Structures”. If you analyze you can see, basic structures built-in Mind mapping is very much tree hierarchical in nature. That’s why Mind Mapping technique can be used directly into your project documentation.
Breakdown structures
Breakdown structures are important document formats throughout Project Management Life Cycle. One can see Work BS, Resource BS, Risk BS, Organizational BS used in most of the Project.
Breakdown structures follow the general principle of life –
“What you think as a big & unachievable can be achieved by breaking it down into smaller pieces & successfully finishing all smaller pieces leads to completion of the big”.
I like to give simple and effective example here. You are about to have a big buffet lunch. If you think of eating all in one stretch, then it is surely unachievable. You are finishing that tasty feast by eating one mouth at a time.
In Project Management, Breakdown structures are hierarchical representation of information based on certain broad element at the higher level and detailing it out in the descending levels (This is what you do exactly in Mind Mapping too!). A breakdown structure has nodes that represent some text attached to it that conveys some specific information. Nodes are connected with branches in a parent-child tree structure that follows parent = sum of all children rule.
Few other general design principles applies to breakdown structures like 1) 100% Rule 2) Mutual exclusive elements 3) Level of detail. Here are few commonly used breakdown structures and their explanations.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) – The WBS is a hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables.
Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) – The resource breakdown structure is a hierarchical representation of resources by category and type.
Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS) – A hierarchical representation of the project organization that illustrates the relationship between project activities and the organizational units that will perform those activities.
Risk Breakdown Structure (RBS) – A hierarchical representation of risks according to their risk categories.